介紹
這一篇是 Java 基本語法介紹的第三篇,我們要來繼續探討程式碼架構。
Vector 類別
Vector 是一種可以自動增減長度的「動態陣列」,屬於 java.util 套件的一部分,它的概念類似於 ArrayList,但 Vector 是執行緒安全 (synchronized) 的版本,因此在多執行緒環境中使用更安全,但效能稍慢一些 。
與 ArrayList 相比的主要差異是 Vector 所有操作方法都加上同步鎖定 (synchronized)。
常用的方法統整:
| 方法 |
功能說明 |
add(E e) |
在尾端新增元素 |
add(int index, E e) |
在指定位置加入元素 |
get(int index) |
取得指定位置的元素 |
remove(int index) |
移除指定位置的元素 |
size() |
回傳目前元素個數 |
capacity() |
回傳目前容量大小 |
clear() |
清空所有內容 |
contains(Object o) |
檢查是否包含指定元素 |
iterator() |
回傳用於遍歷的 Iterator |
範例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| Vector<String> fruits = new Vector<>();
fruits.add("Apple");
fruits.add("Banana");
fruits.add("Mango");
System.out.println(fruits);
System.out.println(fruits.get(1));
fruits.remove("Apple");
System.out.println(fruits.size());
|
例外
例外處理
我們在執行程式的過程中,有時會有發生錯誤的時候,這時我們可以使用例外處理機制來攔截執行期間的錯誤。
以下是常見的例外 (Exception):
| 錯誤代碼 |
意思 |
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException |
陣列索引值超出範圍 |
ArithmeticException |
運算時產生的錯誤,例如除數為 0 |
ArrayStoreException |
指定陣列內容時產生的錯誤 |
ClassCastException |
類別轉換錯誤 |
ClassNotFoundException |
找不到指定的類別 |
CloneNotSupportException |
在類別中使用 clone(),但該類別尚未實作 Cloneable 介面 |
FileNotFoundException |
找不到指定檔案 |
InterruptedException |
另一個執行緒試圖使用 Interrupt() 來中斷已停止的執行緒 |
IOException |
檔案、網路輸入輸出產生的錯誤 |
IllegalArgumentException |
呼叫方法時傳遞錯誤的參數 |
IndexOutOfBoundsException |
索引值超出範圍 |
NullPointerException |
使用物件時,該物件的參考值為 null |
NumberFormatException |
字串轉數字產生的錯誤 |
SecurityException |
違反安全性限制 |
如何判斷錯誤並執行例外處理:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| try {
程式執行區塊
}catch (例外名稱){
例外處理的程式碼區塊
}finally{
最後執行的程式區塊
}
|
範例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| import java.util.InputMismatchException;
import java.util.Scanner;
try (Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in)) {
System.out.print("請輸入分子數:");
int a = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.print("請輸入分母數:");
int b = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println(a + "除以" + b + "等於:" + a / b);
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("錯誤代碼: " + e.getClass().getSimpleName());
System.out.println("除數不能為0");
} catch (InputMismatchException e) {
System.out.println("輸入的數值必須為整數數值");
}
|
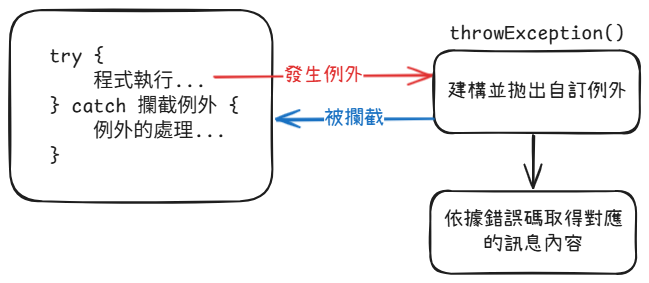
拋出例外 Throw & Throws
程式執行的過程中,所引發的錯誤例外,都是由 Java 的虛擬機 (JVM) 來自動產生錯誤提示的例外。
我們也可以自行產生指定的例外,來提供程式判斷與處理這些例外。
自行產生例外有兩種方式:
throw: 在程式中產生一個例外物件。throws: 宣告一個類別的方法,並指定該方法可以產生一個例外物件。
範例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| try {
String myText = "Hello, World!";
if (myText.equals("Hello, World!")) {
throw new ArithmeticException("自己產生的錯誤例外");
}
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("捕捉到 ArithmeticException: " + e.getMessage());
}
|
如果在方法內發生錯誤,但方法內沒有 try ... catch ... 的例外處理,就可以在方法宣告時使用 throws 將例外產生,讓呼叫該方法的那一層來處理。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| public class Main {
public int divide(int a, int b) throws ArithmeticException {
return a / b;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main t = new Main();
try {
System.out.println(t.divide(10, 0));
} catch (ArithmeticException ex) {
System.out.println("發生運算錯誤");
}
}
}
|
自訂例外
Exception 是一個類別。裡面有各種例外物件的類別型態。如果想要建立自己的例外類別,來處理特殊的情況,可以使用繼承 Exception 類別,產生自訂例外類別。
產生自訂例外類別的方法如下:
1
2
3
4
5
|
class MyException extends Exception {...}
class MyException_2 extends RuntimeException {...}
|
Exception 可用的 Throwable 方法:
| 方法 |
功能 |
回傳值資料型態 |
fillnStackTrace() |
回傳包含完整堆疊追蹤的 Throwable 物件 |
Throwable |
getCause() |
回傳造成例外原因的 Throwable 物件 |
Throwable |
getMessage() / getLocalizedMessage() |
回傳例外訊息說明 |
String |
getStackTrace() |
回傳包含堆疊追蹤的陣列 |
StackTraceTlement[ ] |
initCause(Throwable cause) |
將 cause 當作是例外發生的原因 |
Throwable |
printStackTrace() |
顯示堆疊追蹤 |
void |
printStackTrace(PrintStream ps) |
將堆疊追蹤顯示在 PrintStream 類別串流物件上 |
void |
printStackTrace(PrintWriter pw) |
將堆疊追蹤顯示在 PrintWriter 類別串流物件上 |
void |
setStackTrace(StackTraceElement[] ste) |
設定堆疊追蹤元素由 getStackTrace 的方法回傳,由 printStackTrace 的方法顯示 |
void |
toString() |
回傳簡短的例外描述字串 |
String |
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| class UserException extends Exception {
private String errCode;
private String errMessage;
public UserException(String errCode) {
this.errCode = errCode;
errMessage="這是一個自訂例外!!";
}
public String getErrCode() {
return errCode;
}
public String getMessage() {
return errMessage;
}
}
public class Main {
public void throwUserException() throws UserException {
throw new UserException("001");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main test = new Main();
try {
test.throwUserException();
} catch (UserException e) {
System.out.println("錯誤碼:" + e.getErrCode());
System.out.println("錯誤訊息:" + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
|
Math
Java 將較常使用的數學函式,製作成方法,封裝於 Java.lang 套件中的 Math 類別。屬於 Java 的預設套件,所以 Java 會自動引入該套件。
常數
Math 類別定義了兩個數學常數,分別是自然對數 (E) 與圓周率的 (PI)。
| 常數名稱 |
資料類型 |
值 |
| E |
double |
2.71828182… |
| PI |
double |
3.141592653… |
方法
| 方法 |
功能 |
random() |
隨機數 |
pow(a, b) |
次方 |
sqrt(a) |
平方根 |
min(a, b) |
回傳最小值 |
max(a, b) |
回傳最大值 |
abs(a) |
回傳絕對值 |
toDegrees(angrad) |
回傳弧度的角度 |
toRadians(angdeg) |
回傳角度的弧度 |
sin(a) |
正弦函數 |
cos(a) |
餘弦函數 |
tan(a) |
正切函數 |
asin(a) |
反正弦函數 |
acos(a) |
反餘弦函數 |
atan(a) |
反正切函數 |
exp(a) |
回傳指數 |
log(a) |
log |
log10(a) |
log10 |
使用方式
使用 Math 類別底下的函式,Math.<方法>。
1
2
3
| double value = Math.pow( 2, 10 );
System.out.println( "2 的 10 次方 = " + value);
System.out.println( value + "開根號的結果 = "+Math.sqrt(value));
|
Object
物件的建構
物件是一個參考類型,所以在宣告物件名稱的時候,不會配置實際的記憶體空間。因此,必須要用 new 來建立記憶體空間並將物件指向記憶體位址。
格式如下:
建構子
建構子是類別內的方法,建構子有兩種型態,分別是有參數與無參數型態。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| public class Car {
private String brand;
private String model;
public Car() {
this.brand = "Toyota";
this.model = "Corolla";
}
public Car(String brand, String model) {
this.brand = brand;
this.model = model;
}
public void displayInfo() {
System.out.println("Brand: " + brand + ", Model: " + model);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Car car1 = new Car();
car1.displayInfo();
Car car2 = new Car("Honda", "Civic");
car2.displayInfo();
}
}
|
方法的多載 Overload
在同一個類別中,可以定義多個相同名稱的方法但傳入的參數不同。讓我們可以使用不同的引數組合來呼叫同一功能。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| package com.raylon;
public class Main {
public void sayHello() {
System.out.println("Hello, World!");
}
public void sayHello(String name) {
System.out.println("Hello, " + name + "!");
}
public void sayHello(String name, int times) {
for (int i = 0; i < times; i++) {
System.out.println("Hello, " + name + "!");
}
}
public void sayHello(int times) {
for (int i = 0; i < times; i++) {
System.out.println("Hello");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main obj = new Main();
obj.sayHello();
obj.sayHello("Alice");
obj.sayHello("Bob", 3);
obj.sayHello(2);
}
}
|
參數的「型態」、「數量」或「順序」必須要有一項不同。
This 指標
this 是自己,代表當前的類別或物件,在方法當中可以使用 this.<屬性名稱/方法名稱> 來呼叫當前類別或物件中的屬性或方法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| class Subject {
int subjectNo;
String chiName,engName;
int credit = 2;
Subject(int subjectNo,String chiName,String engName){
this.subjectNo = subjectNo;
this.chiName = chiName;
this.engName = engName;
}
Subject(int subjectNo,String chiName,String engName, int credit){
this(subjectNo, chiName, engName);
this.credit = credit;
}
void display( ){
System.out.printf( "課程: %d-%s (%s), 學分數:%d \n",
subjectNo, chiName, engName, credit );
}
}
class Main {
public static void main(String args[]){
Subject s1=new Subject(112, "運算思維", "Python");
Subject s2=new Subject(111, "程式設計", "java", 3);
s1.display();
s2.display();
}
}
|
繼承
透過繼承,子類別建構的物件會有父類別的特性。
繼承的規則
- 父類別宣告為 final 的屬性或方法,子類別不能覆寫。
- 父類別宣告為 private 的屬性或方法,子類別無法繼承使用。
- 父類別宣告為 abstract 的方法,必須要在子類別內實作。
使用方式
語法:
1
2
3
| class 子類別名稱 extends 父類別名稱 {
子類別的方法
}
|
範例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| class Compute {
public void times (int x, int y){
System.out.println(x+"*"+y+"="+(x*y));
}
public void divided (int x, int y){
System.out.println(x+"/"+y+"="+(float)x/y);
}
}
class Accounting extends Compute{
public void plus (int x, int y){
System.out.println(x+"+"+y+"="+(x+y));
}
public void minus (int x, int y){
System.out.println(x+"-"+y+"="+(x-y));
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
Accounting myObj = new Accounting();
myObj.plus(200,30);
myObj.minus(200,30);
myObj.times(200,30);
myObj.divided(200,30);
}
}
|
建構子的執行順序
會先把父類別建構完畢才會建構子類別。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| class TestA{
TestA( ){ System.out.println("這是類別 A");
}
}
class TestB extends TestA{
TestB( ){
System.out.println("這是繼承類別 A 的類別 B");
}
}
class TestC extends TestB{
TestC( ){
System.out.println("這是繼承類別 B 的類別 C");
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println("【單一繼承的建構子執行順序示範:】");
TestB b = new TestB( );
System.out.println("【多重繼承的建構子執行順序示範:】");
TestC c = new TestC( );
}
}
|
覆寫
如果子類別中的方法名稱、傳遞參數和回傳值類型都與父類別中的方法相同時,就會進行覆寫 (Override)。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
Plane747 CAL=new Plane747();
CAL.setData(4000.5,"藍色");
CAL.setLane(5);
CAL.display();
}
}
class AirPlane{
double fuel;
String color;
public void setData(double fuel, String color){
this.fuel=fuel;
this.color=color;
}
public void display(){
System.out.println("飛機可裝載燃料數量:"+fuel);
System.out.println("飛機顏色:"+color);
}
}
class Plane747 extends AirPlane{
private int airLane;
public void setLane(int airLane){
this.airLane=airLane;
}
public void display(){
System.out.println("747飛機可裝載油料 " + fuel + " 公升");
System.out.println("747飛機的顏色是 " + color);
System.out.println("747飛機起飛的跑道是 " + airLane);
}
}
|
Super 指標
在 Java 中,可以使用 this 代表當前的類別;如果想要使用父類別的方法,就可以使用 super 代表上一層的類別。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| public class Main extends Human{
public static void main(String[] args){
Main crew = new Main( );
crew.setName("張三");
crew.setAge(21);
crew.print();
}
public void print(){
System.out.print("【職員】");
super.print();
}
}
class Human{
private String name;
private int age;
protected void setName(String name){
this.name=name;
}
protected void setAge(int age){
this.age=age;
}
protected void print(){
System.out.printf("姓名:%s, 年齡:%n ", name, age);
}
}
|
多型
多型 (Polymorphism) 是指同一個物件,在不同的情況下,可以表現出不同的行為。目的是讓程式更有彈性、可擴充性、可維護性。主要是透過抽象的類別繼承與介面的實作,讓不同類型的物件可以實作同一個介面,並根據不同的情況呼叫對應的方法。
抽象類別
抽象類別是指含有抽象方法的類別,抽象方法只是事前先宣告方法名稱、參數與回傳的資料型態,還沒有實作。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
| abstract class Animal {
String name;
int age;
public Animal(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
abstract void makeSound();
public void printInfo() {
System.out.println("名字: " + name);
System.out.println("年齡: " + age);
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
public Dog(String name, int age) {
super(name, age);
}
void makeSound() {
System.out.println("汪汪!");
}
}
class Cat extends Animal {
public Cat(String name, int age) {
super(name, age);
}
void makeSound() {
System.out.println("喵喵!");
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal myDog = new Dog("來福", 3);
Animal myCat = new Cat("來喜", 2);
myDog.makeSound();
myDog.printInfo();
myCat.makeSound();
myCat.printInfo();
}
}
|
介面
介面 (interface) 是一個完全沒有任何方法被實作的抽象類別。介面是一個類別,裡面所有宣告的方法都必須是抽象的。因此,在繼承類別時必須實作介面中的所有方法。
語法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| interface 介面名稱 {
[ 修飾語 ] 資料類型 常數名稱 = 值;
......
[ 修飾語 ] 回傳值類型 介面方法名稱(參數, ...);
......
}
class 類別名稱 implements 介面名稱1, 介面名稱2, ... {
實作介面的方法;
}
|
範例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| interface IPet {
public String attr = "可愛";
void skill( );
void action( );
}
class Puppy implements IPet {
public void skill( ) {
System.out.println( attr+",撒嬌");
}
public void action( ) {
System.out.println("追趕跑跳碰");
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
Puppy myPet = new Puppy( );
myPet.skill( );
myPet.action( );
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| interface IRequest {
void execute();
}
class HelloRequest implements IRequest {
private String name;
public HelloRequest(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void execute() {
System.out.println("您好," + name);
}
}
class WelcomeRequest implements IRequest {
private String place;
public WelcomeRequest(String place) {
this.place = place;
}
public void execute() {
System.out.println("歡迎光臨" + place);
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n;
for(int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
n = (int) (Math.random() * 2) +1;
if (n == 1)
doRequest( new HelloRequest("張三"));
else
doRequest(new WelcomeRequest("某大學"));
}
}
public static void doRequest(IRequest request) {
request.execute();
}
}
|
繼承類別與介面
繼承類別使用 extends;繼承介面使用 implements,同時進行繼承類別與介面時要先宣告 extends 再宣告 implements。
語法:
1
2
3
| class 類別名稱 extends 父類別名稱 implements 介面名稱1, 介面名稱2, ... {
實作介面的方法;
}
|
範例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| interface Engine {
public void start( );
public void stop( );
}
class Gearbox {
public void shiftUp( ) {
System.out.println("進檔");
}
public void shiftDown( ) {
System.out.println("退檔");
}
}
class Car extends Gearbox implements Engine {
public void start( ) {
System.out.println("發動引擎");
}
public void stop( ) {
System.out.println("停止引擎");
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Car myCar = new Car( );
myCar.start( );
myCar.shiftUp( );
myCar.shiftDown( );
myCar.stop( );
}
}
|

